9 Essential Database Management Best Practices for 2025

In today's data-driven world, your database is more than just a storage repository; it's the operational core of your business. From customer information to critical transactions, its health, security, and efficiency directly impact your bottom line. However, managing this critical asset is complex. Minor oversights can lead to sluggish performance, critical data loss, or devastating security breaches. That's why adopting robust database management best practices is not just a technical task-it's a strategic business imperative.
This guide cuts through the noise to provide a curated roundup of nine essential practices that will fortify your data infrastructure. We'll move beyond generic advice to offer actionable insights, real-world examples, and specific implementation steps. You will learn how to properly structure your data, secure sensitive information, and ensure high performance under pressure.
From regular backups and recovery planning to advanced performance tuning and scalability, each section is designed to be a practical, standalone guide. By implementing these proven strategies, you can build a resilient, efficient, and secure database that supports your business goals for 2025 and beyond. Let’s dive into the practices that transform a database from a simple utility into a powerful competitive advantage.
1. Regular Database Backups and Recovery Planning
Effective database management best practices begin with a non-negotiable foundation: a robust and regularly tested backup and recovery plan. This strategy involves more than just copying data; it's a comprehensive process of creating automated, scheduled backups and rigorously testing recovery procedures. This ensures your organization can swiftly restore operations after any data loss event, whether from hardware failure, data corruption, cyber attacks, or simple human error.

A well-rounded approach combines different backup types, such as full, differential, and incremental backups, to balance speed and resource usage. For instance, Salesforce implements real-time backup replication for its enterprise customers, guaranteeing a minimal Recovery Point Objective (RPO). The infamous 2017 GitLab incident, where multiple backup systems failed simultaneously, serves as a stark reminder that creating backups is only half the battle; they are worthless without proven, repeatable restoration procedures.
Key Implementation Steps
To build a reliable safety net for your data, focus on these actionable steps:
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data on two different types of media, with one copy stored off-site. This diversification protects against localized disasters like fires or floods. For a broader understanding of protecting your information, consider referring to a comprehensive guide to backing up data.
- Test Restorations Quarterly: Don't assume your backups work. Regularly schedule and execute restoration tests in a sandbox environment to verify data integrity and practice your recovery process.
- Automate and Monitor: Automate both the backup creation and the monitoring process. Set up alerts for any backup failures to ensure immediate attention and resolution.
- Encrypt Everything: Secure your backups by encrypting them both at rest (in storage) and in transit (while being copied to another location) to prevent unauthorized access.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/S0KZ5iXTkzg" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
2. Database Indexing Optimization
A cornerstone of effective database management best practices is the strategic creation and maintenance of indexes. Think of an index as the index in the back of a book; instead of scanning every page (a full table scan), the database can quickly look up the location of the data it needs. This practice dramatically accelerates query performance, which is crucial for applications that rely on fast data retrieval. Proper indexing involves analyzing query patterns and creating the right type of index to match the workload, ensuring your database remains responsive as data volume grows.
Strategic indexing is the secret behind the performance of many large-scale applications. For example, Stack Overflow famously reduced critical query times from over 20 seconds to under one second by optimizing indexes on its massive database. Similarly, Airbnb's search functionality relies on carefully crafted composite indexes on location, dates, and property attributes to deliver results instantly. These examples highlight that while indexing consumes storage and can slow down write operations (like INSERTs and UPDATEs), the performance gains for read-heavy workloads are indispensable.
Key Implementation Steps
To boost your database's query performance through indexing, focus on these actionable steps:
- Analyze Your Queries: Use tools like
EXPLAINorANALYZEto identify slow-running queries and determine which columns are most frequently used inWHERE,JOIN,ORDER BY, andGROUP BYclauses. These are prime candidates for indexing. - Index Foreign Keys: Always create indexes on foreign key columns. This simple step significantly speeds up
JOINoperations, which are common in relational databases and often a major source of performance bottlenecks. - Use Covering Indexes: For frequently executed queries that retrieve only a few specific columns, create a "covering index." This type of index includes all the required columns, allowing the database to answer the query using only the index, without ever touching the table data.
- Monitor and Prune: Regularly monitor index usage statistics to identify indexes that are rarely or never used. Unused indexes waste storage space and add unnecessary overhead to write operations, so they should be dropped. You can learn more about index maintenance from resources like the PostgreSQL documentation on routine maintenance.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/fsG1M_B9A7E" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
3. Database Security and Access Control
Robust database management best practices must prioritize comprehensive security and tightly controlled access. This involves a multi-layered defense strategy that combines strong authentication, granular authorization, and end-to-end encryption to shield sensitive data. The goal is to protect information from unauthorized access, breaches, and compliance violations, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality at all times.

This proactive approach is crucial for preventing catastrophic data loss and maintaining regulatory compliance. The 2017 Equifax breach, which exposed the personal data of 147 million people, underscores the devastating consequences of inadequate security measures. Conversely, financial institutions successfully use database activity monitoring and tokenization to meet strict PCI-DSS standards for credit card data, while providers like Google Cloud build trust by making powerful encryption a default feature for all customer databases.
Key Implementation Steps
To build a secure fortress around your database, concentrate on these critical actions:
- Implement the Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users and applications the absolute minimum permissions required to perform their jobs. Avoid using shared or generic accounts.
- Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit: Protect data wherever it is. As part of robust database security, comprehending the crucial the role of encryption in information security is vital for safeguarding data on disk and as it moves across networks.
- Prevent SQL Injection: Use parameterized queries or prepared statements in your application code. This is a fundamental defense against one of the most common and damaging web application attacks.
- Regularly Audit and Monitor Access: Continuously review user permissions, audit logs for suspicious activity, and implement database activity monitoring (DAM) tools for real-time threat detection.
- Keep Software Patched: Promptly apply all security patches and updates for your database management system (DBMS) and operating system to close known vulnerabilities.
4. Database Performance Monitoring and Tuning
Proactive database performance monitoring and tuning are critical for maintaining a responsive and reliable application experience. This practice involves continuously tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like query response times, CPU usage, and memory consumption to identify and resolve bottlenecks before they impact users. It’s a cyclical process of measuring, analyzing, and optimizing database configurations, queries, and resource allocation to ensure efficiency as data volumes and workloads evolve.
Effective monitoring goes beyond just keeping the lights on; it directly impacts user satisfaction and operational costs. For example, LinkedIn leverages custom performance monitoring to manage billions of daily queries, ensuring a smooth user experience. Similarly, Shopify constantly monitors query performance across its vast network of merchant databases to guarantee consistent e-commerce platform speed. These examples highlight how diligent performance management is a cornerstone of scalable, high-performing systems and a key component of effective database management best practices.
Key Implementation Steps
To transform your database from a potential bottleneck into a performance asset, integrate these actionable steps:
- Establish a Performance Baseline: Before you can identify problems, you must understand normal behavior. Document key metrics like average query response times, CPU utilization, and I/O rates during typical operations to create a baseline for comparison.
- Automate Alerting: Set up automated alerts for critical thresholds. Get notified when response times exceed a specific limit, CPU usage remains high, or available connections run low. Tools like Datadog and New Relic excel at this.
- Analyze Slow Query Logs: Regularly review slow query logs to identify inefficient or resource-intensive queries. Optimizing even a single, frequently-run query can yield significant performance gains across the entire application.
- Integrate Application and Database Monitoring: Monitor database performance in conjunction with application-level metrics. An Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tool can help correlate a slow API endpoint with a specific database query, dramatically speeding up root cause analysis.
5. Database Normalization and Schema Design
A well-designed schema is the architectural blueprint for a scalable and maintainable database. This foundational practice involves database normalization: the process of organizing columns and tables to minimize data redundancy and improve data integrity. By structuring data according to established normal forms (like 1NF, 2NF, and 3NF), you create a logical, efficient design that prevents data anomalies and simplifies future modifications, making it a critical aspect of database management best practices.
This methodical approach ensures that each piece of information is stored in only one place, preventing inconsistencies that arise when the same data is duplicated across multiple tables. For example, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems like SAP rely on highly normalized, complex schemas to manage thousands of related tables with absolute data consistency. Conversely, e-commerce giants like Amazon might strategically denormalize parts of their product catalog, trading a bit of redundancy for faster query performance and a better user experience, demonstrating the need for a balanced approach.
Key Implementation Steps
To design a robust and efficient database schema, concentrate on these core principles:
- Start with 3NF as a Baseline: Aim for at least Third Normal Form (3NF) to eliminate most data redundancy issues without overly complicating the design. This provides a strong foundation for data integrity.
- Document with ER Diagrams: Before writing any code, create an Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram. This visual model helps you and your team understand table relationships, constraints, and the overall data structure.
- Use Surrogate Keys: Implement auto-incrementing integers or UUIDs as primary keys instead of natural keys (like email addresses). Surrogate keys are stable, efficient, and prevent update complexities if the natural data changes.
- Define Proper Constraints: Use foreign key constraints to enforce referential integrity between tables. Implement
NOT NULL,UNIQUE, andCHECKconstraints to ensure the data entered into your database is always valid and consistent.
6. Transaction Management and ACID Compliance
Proper transaction management is a cornerstone of reliable database operations, ensuring data integrity even in highly concurrent environments. This best practice revolves around adhering to the ACID properties: Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. Implementing ACID-compliant transactions guarantees that a group of database operations is treated as a single, indivisible unit. This prevents partial updates and data corruption, which is critical for maintaining a trustworthy and consistent state.
This principle is vital in systems where accuracy is non-negotiable. For example, a banking application uses an atomic transaction to ensure that when money is transferred, the debit from one account and the credit to another either both succeed or both fail together. Similarly, e-commerce platforms like Shopify wrap inventory updates and order creation in a single transaction to prevent overselling popular items. The work of transaction processing pioneers like Jim Gray laid the foundation for these reliable systems, making ACID compliance a fundamental expectation in modern database management best practices.
Key Implementation Steps
To effectively manage transactions and ensure data integrity, focus on these actionable steps:
- Keep Transactions Short: Design transactions to be as brief as possible. Shorter transactions hold locks for less time, which reduces contention and improves overall system performance.
- Choose Appropriate Isolation Levels: Don't default to the strictest level, like Serializable, unless necessary. Start with
Read Committedfor most applications as it provides a good balance between consistency and concurrency. - Implement Robust Error Handling: Every transaction block must include comprehensive error handling that triggers a
ROLLBACKcommand. This ensures that any failed operation returns the database to its previous consistent state. - Avoid External Calls Within Transactions: Never place long-running operations, user interactions, or external API calls inside a transaction. These can hold locks for an unpredictable amount of time, leading to deadlocks and poor performance.
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/5yD4YV1O32U" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
7. Database Documentation and Change Management
A well-managed database is a well-documented one. This practice involves creating and maintaining comprehensive documentation for schemas, configurations, and procedures while implementing a structured change management process. This ensures that every modification, from a simple column addition to a complex procedural change, is tracked, tested, and approved, fostering reliability, team collaboration, and a clear audit trail.
Neglecting this area leads to knowledge silos and high-risk deployments. In contrast, companies like Etsy use database migration tools with integrated peer reviews, enabling hundreds of safe schema changes daily. Similarly, Spotify uses Flyway for database version control, which allows for traceable and consistent schema evolution across its many microservices. These examples highlight how robust documentation and change management are cornerstones of modern database management best practices, preventing chaotic development cycles and ensuring system integrity.
Key Implementation Steps
To build a transparent and stable database environment, focus on these actionable steps:
- Version Control All Changes: Store all database scripts (DDL, DML, stored procedures) in a version control system like Git, alongside your application code. This provides a complete history of every change.
- Implement a Peer Review Process: Mandate that all proposed schema and configuration changes are reviewed by at least one other team member before being merged and deployed, catching potential errors early.
- Automate Documentation Generation: Use tools like SchemaSpy or dbdocs.io to automatically generate data dictionaries and relationship diagrams from your database metadata, keeping documentation current with minimal effort.
- Plan for Rollbacks: For every change you plan to deploy, document a clear and tested rollback procedure. This is your safety net if a deployment introduces unforeseen problems in production.
8. Regular Database Maintenance and Optimization
Proactive database management best practices extend beyond immediate security and performance tuning to encompass routine, preventative care. Regular database maintenance and optimization are akin to scheduled servicing for a high-performance engine; they keep the system running efficiently and prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures. This involves establishing a consistent schedule for tasks like index defragmentation, updating statistics, running integrity checks, and managing log files to ensure long-term database health and stability.
Neglecting maintenance leads to performance degradation, storage bloat, and potential data corruption. For example, Amazon RDS addresses this by offering configurable, automated maintenance windows for patching and optimization, ensuring systems remain healthy with minimal manual intervention. Similarly, Microsoft SQL Server provides maintenance plans that can be automated to rebuild indexes and update statistics nightly. Tools like Ola Hallengren's maintenance solution have become industry standards for SQL Server, providing intelligent and customizable scripts that are far more effective than basic, built-in plans. These routines prevent emergencies and maintain optimal performance over time.
Key Implementation Steps
To establish an effective maintenance routine for your database, focus on these core actions:
- Schedule During Off-Peak Hours: Run maintenance jobs during periods of low user activity, such as 2-5 AM local time, to minimize impact on system performance and user experience.
- Manage Index Fragmentation: Regularly check index fragmentation. Rebuild indexes with over 30% fragmentation and reorganize those with 10-30% to improve query speed.
- Update Statistics and Check Integrity: Update database statistics weekly or after significant data changes to help the query optimizer create efficient execution plans. Run integrity checks (e.g., DBCC CHECKDB) at least monthly to detect and address potential data corruption early.
- Automate and Monitor: Use built-in schedulers like SQL Server Agent or cron jobs to automate all maintenance tasks. Critically, set up alerts to notify administrators of any job failures so they can be addressed immediately.
9. Scalability Planning and Database Architecture
Effective database management best practices must anticipate future growth. Scalability planning involves designing a database architecture that can gracefully handle increasing data volumes and user traffic without significant performance degradation or costly re-engineering. This forward-thinking approach ensures your system remains performant and reliable as your business expands, preventing growth from becoming a technical crisis. It's about building a foundation that can evolve.
Implementing a scalable architecture often involves strategies like horizontal scaling (sharding), vertical scaling (upgrading hardware), and creating read replicas to offload queries. For example, Instagram famously uses sharding with PostgreSQL to manage its immense dataset of photos and interactions, while Pinterest migrated to sharded MySQL clusters to handle over 200 billion pins. These strategies demonstrate how proactive architectural decisions support massive, global-scale operations, ensuring a smooth user experience even under extreme load.
For a quick reference, this summary box highlights the core strategies for building a scalable database system.
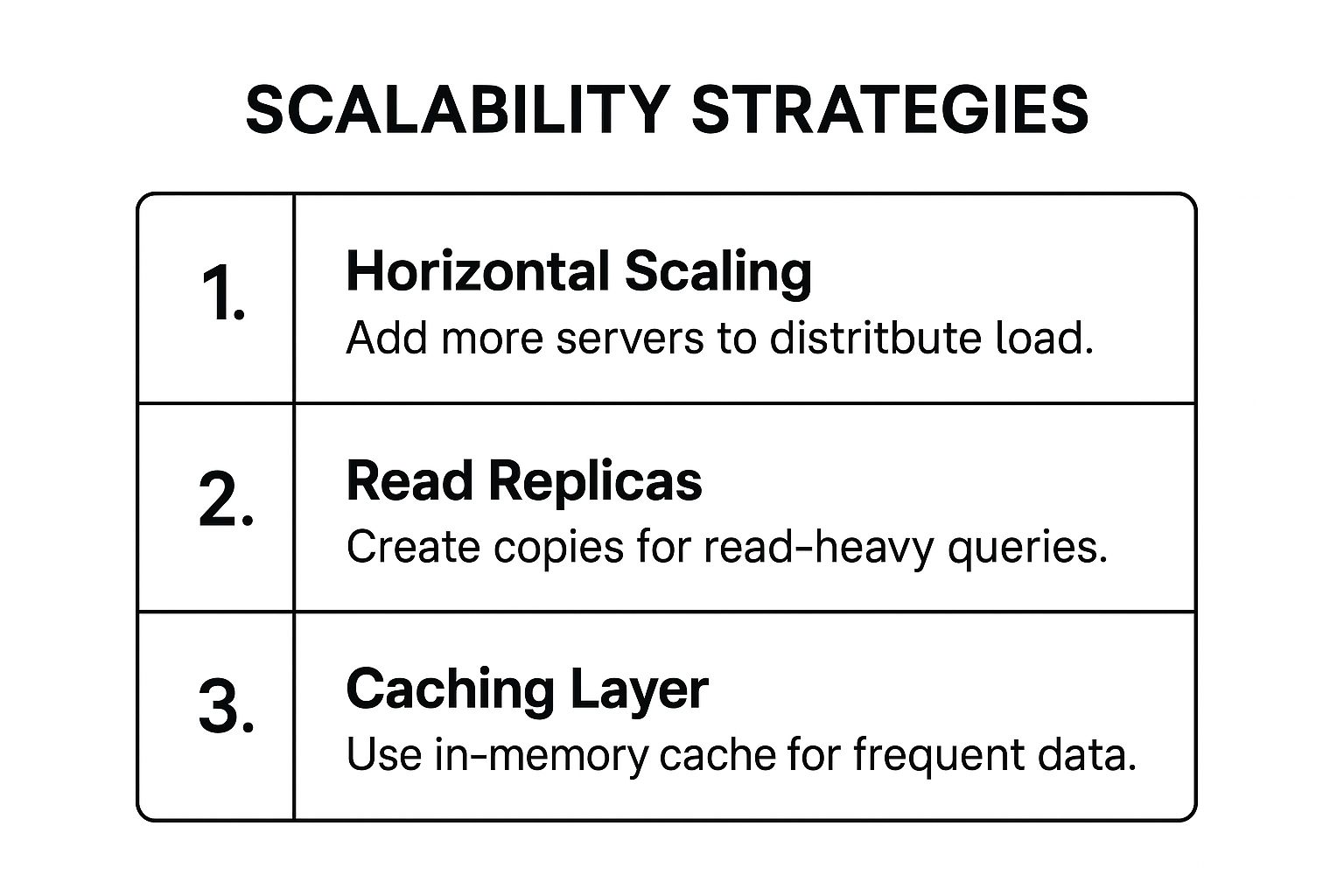
These three pillars, horizontal scaling, read replicas, and caching, form the basis of a modern, resilient database architecture capable of adapting to changing demands.
Key Implementation Steps
To build a database that scales with your business, integrate these actionable steps into your strategy:
- Plan Early, But Don't Over-Engineer: Design for scalability from the start, but implement solutions as needed. Begin with a solid design and introduce components like read replicas or caching layers when performance metrics indicate they are necessary.
- Implement a Caching Layer: Use an in-memory cache like Redis or Memcached to store frequently accessed, rarely changed data. This dramatically reduces read load on your primary database and improves response times.
- Utilize Read Replicas: Offload read-heavy workloads, such as reporting and analytics, to one or more read replicas. This frees up your primary database to handle critical write operations, improving overall system throughput.
- Choose Shard Keys Carefully: When implementing horizontal scaling (sharding), select a shard key that evenly distributes data and traffic across servers. A poor choice can lead to "hotspots," where one shard is overloaded while others are idle.
9 Key Database Management Best Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Database Backups and Recovery Planning | Medium-High: scheduling, testing, managing versions | High: storage, infrastructure, regular testing | Reliable data restoration; disaster recovery; compliance | Critical data protection and business continuity | Ensures rollback, meets compliance, minimizes downtime |
| Database Indexing Optimization | Medium: requires analysis, ongoing tuning | Moderate: additional storage, monitoring tools | Significant query performance improvement | High-read workloads; query-heavy applications | Drastically faster queries, better resource usage |
| Database Security and Access Control | High: complex security policies, ongoing monitoring | Moderate-High: encryption, audit tools, expertise | Data breach prevention; compliance adherence | Sensitive data protection; regulated industries | Protects data, ensures compliance, audit trails |
| Database Performance Monitoring and Tuning | Medium-High: continuous monitoring and analysis | Moderate-High: monitoring tools, expert analysis | Proactive issue detection; optimized performance | Dynamic workloads; large-scale applications | Improves user experience; reduces downtime |
| Database Normalization and Schema Design | Medium: requires expertise and planning | Low-Moderate: design phase focus | Data integrity; reduced redundancy; maintainability | Long-term maintainability; data consistency | Removes redundancy; simplifies updates |
| Transaction Management and ACID Compliance | High: complex concurrency and isolation management | Moderate: transaction overhead and monitoring | Ensured data consistency and atomic operations | Financial, critical systems; multi-user environments | Prevents corruption; supports complex operations |
| Database Documentation and Change Management | Medium: requires process and discipline | Low-Moderate: documentation tools, version control | Improved team collaboration; safer changes | Teams with frequent schema changes; compliance | Reduces errors; audit trails; improves onboarding |
| Regular Database Maintenance and Optimization | Medium: scheduled routines and checks | Moderate: downtime windows, automation tools | Maintained performance; prevents degradation | Long-term database health; production environments | Prevents issues; optimizes storage and queries |
| Scalability Planning and Database Architecture | High: complex design and ongoing adjustments | High: infrastructure, monitoring, expertise | Scalable, high-availability systems | Growing data/user base; globally distributed apps | Supports growth; high availability; fault tolerance |
From Theory to Action: Your Next Steps in Database Mastery
We've explored a comprehensive framework of nine essential principles that form the bedrock of effective data management. From the non-negotiable safety net of regular backups and recovery planning to the forward-thinking strategy of scalability and architecture design, each practice is a critical component in building a robust, secure, and high-performing data environment.
Navigating these concepts can feel overwhelming, but mastery is a journey, not a destination. The goal is not to implement all nine practices overnight, but to embark on a path of continuous improvement. The power of these database management best practices lies in their interconnectedness. A well-designed schema (Normalization) is easier to secure (Access Control), performs better when indexed correctly (Indexing Optimization), and is more adaptable for future growth (Scalability Planning).
Turning Knowledge into Actionable Strategy
The true value is realized when you move from passive understanding to active implementation. Your immediate next step is to assess your current operations against the best practices discussed. Where are the most significant gaps? Where do you face the most immediate risks or performance bottlenecks?
To make this process manageable, adopt a phased approach:
- Identify Your Biggest Pain Point: Is your application slow? Start with Performance Monitoring and Tuning. Are you worried about data loss? Solidify your Backup and Recovery Plan. Pinpointing the most urgent issue provides a clear starting point and delivers the most immediate impact.
- Create a Prioritized Roadmap: Select two or three key areas to focus on for the next quarter. For instance, you might decide to first implement stricter Database Security and Access Control policies, then move on to optimizing key queries through Database Indexing.
- Document and Standardize: As you make improvements, formalize them. Update your Database Documentation and Change Management processes. This ensures consistency and prevents the same issues from recurring, especially as your team grows.
The Strategic Value of a Well-Managed Database
Ultimately, mastering these database management best practices transforms your data from a simple storage repository into a strategic business asset. A well-managed database improves application performance, leading to better user experiences. It enhances data integrity, which allows for more reliable business intelligence and decision-making. Most importantly, it secures your most valuable information, protecting your organization's reputation and bottom line.
By consistently applying these principles, you are not just managing data; you are building a resilient foundation for innovation and growth. Every step you take to improve your database health is an investment in the long-term success and stability of your entire operation. Your data holds the key to future opportunities, and disciplined management is how you unlock its full potential.
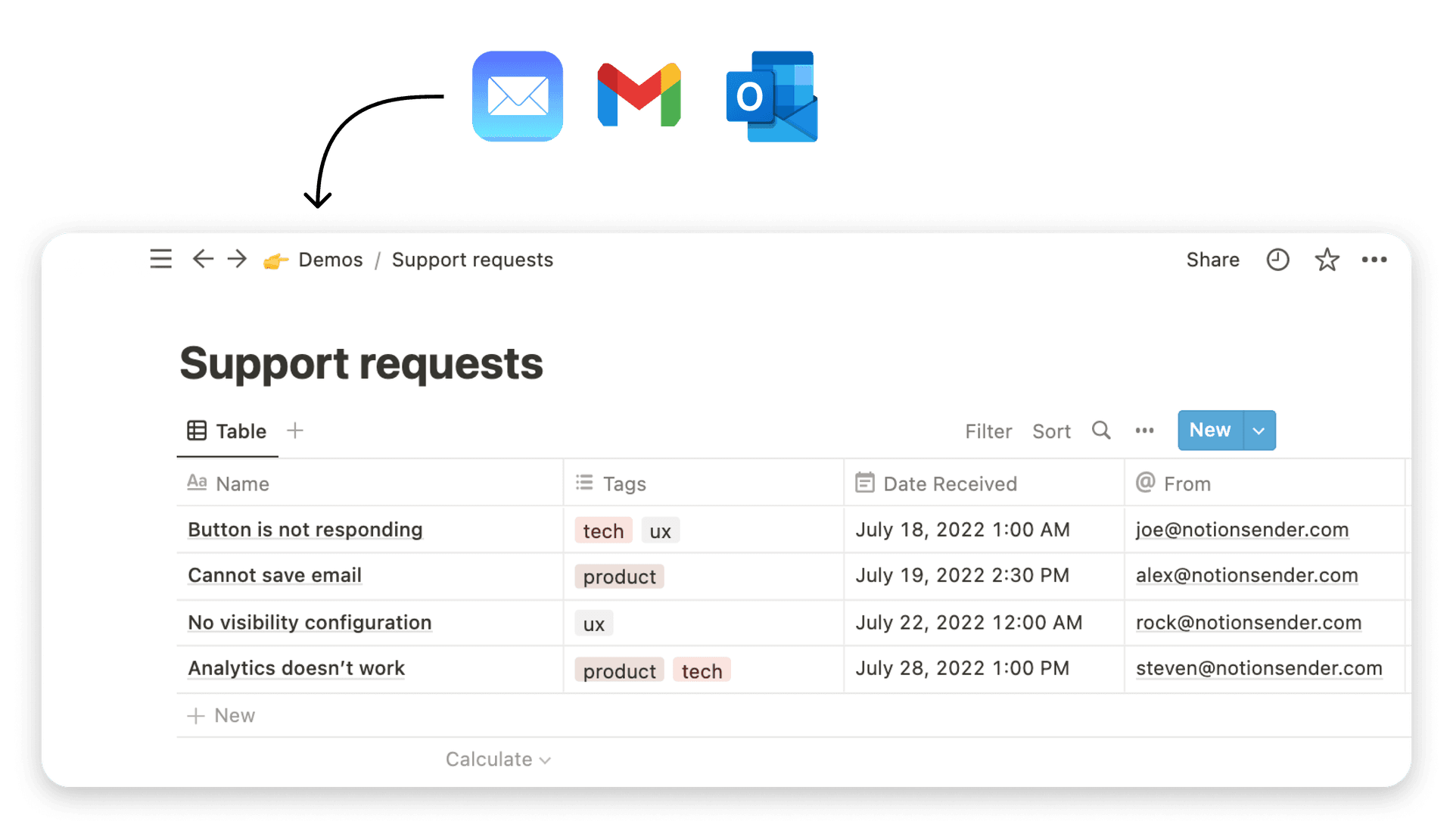
Ready to streamline how you capture information directly into your database? NotionSender allows you to send emails directly to your Notion databases, turning your inbox into a powerful, integrated part of your data management workflow. Enhance your organizational efficiency and centralize critical communications by trying NotionSender today.